Pancreatitis Model
If you are looking for reliable and experienced assistance in conducting preclinical studies in pancreatitis, Creative Bioarray can help. We offer top-notch consultancy services and preclinical models for pancreatitis to help you make informed decisions based on solid data. With our scientific expertise in pancreatitis and extensive experience in animal models, you can trust us to provide you with the best possible support to achieve your research goals.
Chronic and acute pancreatitis are prevalent gastrointestinal conditions that significantly impact morbidity and life expectancy. Despite advancements in supportive care over the past two decades, there remains a dearth of specific and effective pharmacological treatments, primarily due to the incompletely understood pathobiology of the disease.
Experimental animal models have served as valuable tools in pancreatitis research for over a century. In recent years, rodent models (particularly rats and mice) have become the most commonly utilized in pancreatitis studies. These animals are relatively inexpensive to maintain, easy to manipulate, widely accessible, and capable of inducing moderate to severe pancreatic injury. These experimental models not only offer an avenue for mechanistic studies but also facilitate the development of therapeutic strategies, thus paving the way for potential improvements in the management and treatment of pancreatitis.
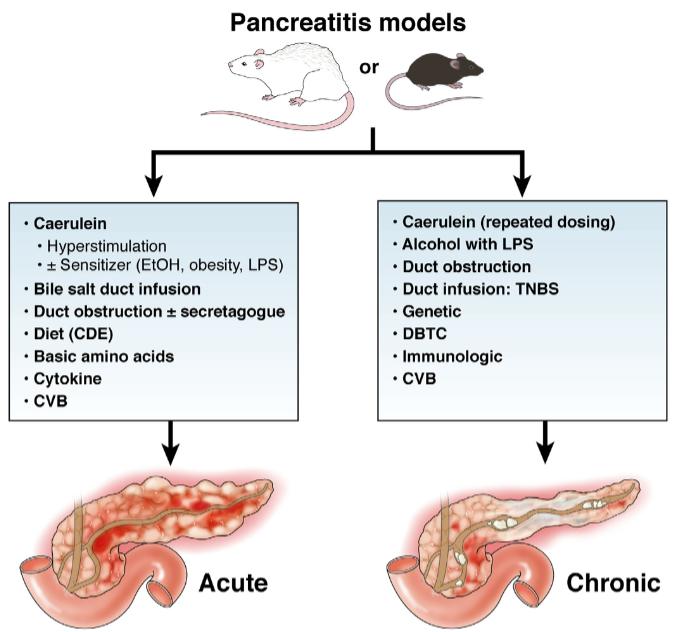 Fig. 1 Rodent models most commonly used to study acute and chronic pancreatitis.
Fig. 1 Rodent models most commonly used to study acute and chronic pancreatitis.
Our Animal Models of Pancreatitis
For pancreatitis research, there are a number of well-characterized animal models. As a research partner specialized in designing pharmacology and efficacy studies for different digestive diseases, Creative Bioarray can utilize the following models for the evaluation of potential therapeutics:
- Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis Model
- Sodium Taurocholate-Induced Pancreatitis Model
- Dibutyltin Dichloride (DBTC) Induced Pancreatitis Model
Example Data
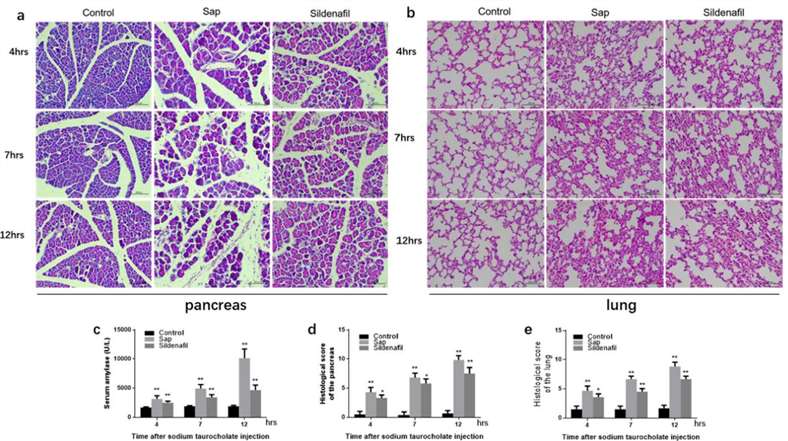 Fig. 2 Morphological changes and histopathological score of SAP-ALI. H&E sections were examined by light microscopy (original magnification, 200×). Neutrophil infiltration, hemorrhage, necrosis and edema in pancreas tissues were observed. In lung tissues, hemorrhage, neutrophil infiltration and alveolar wall thickening were observed (a–b). The pathological scores of pancreas and lung (d–e). Serum amylase (c).
Fig. 2 Morphological changes and histopathological score of SAP-ALI. H&E sections were examined by light microscopy (original magnification, 200×). Neutrophil infiltration, hemorrhage, necrosis and edema in pancreas tissues were observed. In lung tissues, hemorrhage, neutrophil infiltration and alveolar wall thickening were observed (a–b). The pathological scores of pancreas and lung (d–e). Serum amylase (c).
References
- Fang, D., et al. Effects of sildenafil on inflammatory injury of the lung in sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis rats. International immunopharmacology, 2020, 80: 106151.
- Yang, X., et al. Experimental acute pancreatitis models: history, current status, and role in translational research. Frontiers in Physiology, 2020, 11: 614591.
- Lerch, M.M., Gorelick, F.S. Models of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(6): 1180-1193.

